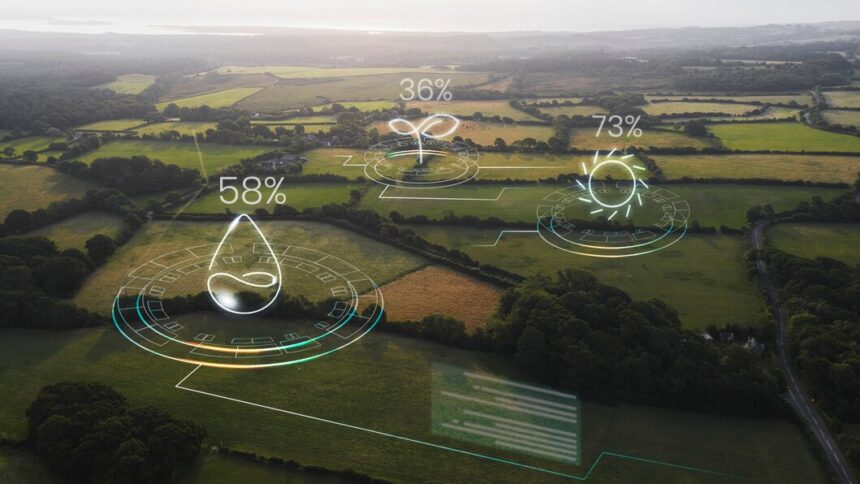
In the ever-evolving landscape of agriculture, South African farmers face numerous challenges, from unpredictable weather patterns to fluctuating market demands. To thrive in such a dynamic environment, farmers must adopt modern technologies that improve efficiency and productivity. One such innovation is the use of GPS (Global Positioning System) for precision farming.
Precision farming, also known as precision agriculture, involves using technology to gather real-time data and make informed decisions. GPS plays a crucial role in this by enabling farmers to map their fields, track resources, and optimize crop yields with minimal waste. Here’s how South African farmers can benefit from using GPS in their farming practices.
1. Field Mapping and Soil Analysis
GPS technology allows farmers to create highly accurate maps of their fields. This enables precise measurements of land area, which is essential for planning planting and harvesting operations. With these maps, farmers can also perform soil sampling more effectively, determining soil nutrient levels, pH balance, and moisture content. This data helps farmers apply fertilizers and water in the right amounts, reducing waste and improving crop health.
Tip: Use GPS to divide your fields into manageable zones based on soil variability. This ensures that crops receive tailored care according to their specific soil needs.
2. Optimized Planting and Seeding
By using GPS-enabled tractors and planting equipment, farmers can automate the planting process with pinpoint accuracy. This precision ensures that seeds are planted at the correct depth and spacing, resulting in uniform growth and reduced seed waste. GPS technology also eliminates overlaps or gaps in planting, which can lead to uneven crop development.
Tip: Combine GPS with other technologies like variable rate seeding (VRS) to adjust seed rates based on soil conditions, further optimizing yields.
3. Efficient Irrigation Management
Water scarcity is a growing concern in many parts of South Africa, making efficient water usage critical for sustainable farming. GPS technology can help farmers monitor water usage and develop efficient irrigation schedules. By mapping areas that require more or less water, GPS ensures that irrigation systems apply the right amount of water where it is needed most.
Tip: Consider using GPS in conjunction with soil moisture sensors to provide real-time data on water levels, helping you adjust irrigation systems for maximum efficiency.
4. Improved Fertilizer and Pesticide Application
GPS technology can be used to create application maps that detail the precise locations where fertilizers and pesticides should be applied. This minimizes over-application, reduces chemical runoff into water systems, and cuts down on costs. Farmers can also apply chemicals only in areas that need them, reducing their environmental impact.
Tip: Incorporate variable rate technology (VRT) with GPS to control the exact amount of fertilizer or pesticide being applied in different parts of the field, leading to cost savings and better crop health.
5. Enhanced Harvesting Efficiency
During harvest, GPS can be used to guide machinery such as combines or harvesters with extreme precision. This reduces crop losses by ensuring that the equipment operates efficiently within the designated boundaries. Farmers can track the progress of their harvest in real-time, allowing them to make adjustments if necessary and improve overall productivity.
Tip: Use GPS data from previous seasons to analyze which areas of the field produced the best yields and adjust future planting and harvesting strategies accordingly.
6. Real-Time Monitoring and Data Analysis
One of the most significant benefits of GPS in farming is its ability to provide real-time data on farm operations. With GPS tracking, farmers can monitor the location of their machinery, equipment, and workers, ensuring that tasks are completed efficiently and on time. This also helps in maintaining safety on large farms by tracking the movement of vehicles and personnel.
Tip: Use GPS data to keep detailed records of field conditions, planting dates, and harvest yields. Over time, this data can help you spot trends and make informed decisions for future seasons.
7. Reduced Fuel and Labour Costs
GPS-enabled equipment can follow the most efficient paths across the field, reducing the time spent on tasks such as tilling, planting, and harvesting. This leads to reduced fuel consumption and lower labor costs, as machinery can complete tasks faster and more accurately.
Tip: Plan out your fieldwork using GPS-based software that designs the shortest and most effective routes for your equipment.
8. Better Farm Management and Sustainability
Precision farming using GPS technology promotes sustainability by reducing the use of natural resources such as water, fuel, and fertilizers. By optimizing resource allocation, farmers can achieve higher yields while minimizing their environmental footprint. This is particularly important as the agricultural sector seeks to balance productivity with the growing demand for sustainable practices.
Tip: Monitor your carbon footprint by using GPS data to track resource usage and identify areas where you can improve sustainability.
Incorporating GPS technology into farming practices is no longer a luxury but a necessity for South African farmers who want to stay competitive and sustainable. Precision farming using GPS can lead to better resource management, increased crop yields, and cost savings. As farmers continue to face challenges from climate change, water scarcity, and rising input costs, adopting GPS technology will provide them with the tools needed to thrive in a rapidly changing agricultural landscape.
By embracing GPS, South African farmers can improve efficiency, reduce waste, and ensure that their farms remain profitable and sustainable for future generations.
Join 'Farmers Mag' WhatsApp Channel
Get the latest Farming news and tips delivered straight to your WhatsApp
CLICK HERE TO JOIN